What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is an emerging strategy for website and content optimization, similar to SEO, that focuses on making your content more authoritative and trusted by large language models (LLMs). This increases visibility, traffic, and conversions for your brand, originating from AI-generated responses in services such as ChatGPT and Perplexity.
Generative Engine Optimization is also sometimes referred to as AI Optimization (AIO) or Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) but recently, GEO has emerged as the most relevant terminology.
Real-world Generative Engine Optimization example
🧠 User Query Prompts the LLM System
- A user types into an AI chatbot like ChatGPT or Perplexity:
- “What are the fastest NoSQL databases in 2025?”
- The LLM begins processing this query by:
- Understanding the intent: speed/performance comparison of NoSQL databases
- Identifying key concepts: NoSQL, fastest, benchmarks, 2025
🔎 LLM Starts Synthesizing a Response
- The model scans its training data and recently indexed web content (if it’s a tool like Perplexity or Google’s AI Overview that references the internet to generate answers) looking for:
- Authoritative articles, blog posts, benchmarks, documentation
- Structured content that clearly ranks or compares NoSQL databases
- Example content that gets favored:
- A blog post titled “Top 7 Fastest NoSQL Databases Compared [2025 Benchmark]”
- Well-formatted tables or bullet lists showing database names, speeds, pros/cons
- Clear titles, H2s, metadata that reflect the query language
- Example content that gets favored:
🤖 LLM Generates a Human-Readable Answer
-
- The AI synthesizes the info into something like:
- “Some of the fastest NoSQL databases in 2025 include Redis, Cassandra, and Couchbase. Redis is often praised for its in-memory speed, while Cassandra is known for scalability.”
- If your content is GEO’d (GEO-optimized), it may be:
- Quoted directly, especially if it contains standout phrasing or clear rankings
- Cited inline (like a footnote or [source])
- The AI synthesizes the info into something like:
🔗 User Sees the Response + Citation
- In tools like Perplexity, ChatGPT (with web browsing), or Google’s AI Overview:
- A clickable link is provided to your site:
- “Source: yourblog.com/top-nosql-databases-2025”
- A clickable link is provided to your site:
- If the content is well-cited and matches the intent, users are more likely to:
- Discover and eventually trust your brand as an authority
- Click through to read more
- Convert on any CTAs
✅ Generative Engine Optimization That Helped This Happen
- Keyword-rich, intent-matching title (e.g., “Fastest NoSQL Databases [2025 Review]”)
- Structured comparison table with performance metrics
- Clear, quotable content (short paragraphs, skimmable bullets)
- Author name, date, and domain authority (trust signals)
How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?
From a strategic point of view, the activities involved in optimizing a website and content to rank for keywords on Google/Bing (SEO) are currently very similar to optimizing those things for AI-generated responses (GEO). The key difference is that traditional search algorithms retrieve results by matching keywords and ranking web pages based on factors like backlinks, metadata, and relevance signals.
In contrast, LLMs generate answers by understanding the context and intent of a query, then synthesizing information from a vast range of sources (the internet plus vast amounts of uploaded training data) — rather than just pointing to links. That means your brand’s visibility increasingly depends on how well your content is structured, understood, and cited by these models.
Why is GEO becoming increasingly important?
As the rules of SEO evolve rapidly, it’s no longer just about ranking on Google or Bing.
With more people turning to generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity to get direct answers, the game is changing. If a brand is able to consistently show up as a source of information in AI-generated answers, the trust and affinity for that brand will increase exponentially, leading to more traffic and eventually sales. It should be noted that despite the meteoric rise of these AI tools, the vast majority of internet users still turn to Google for most of their searches, according to this study from SparkToro:
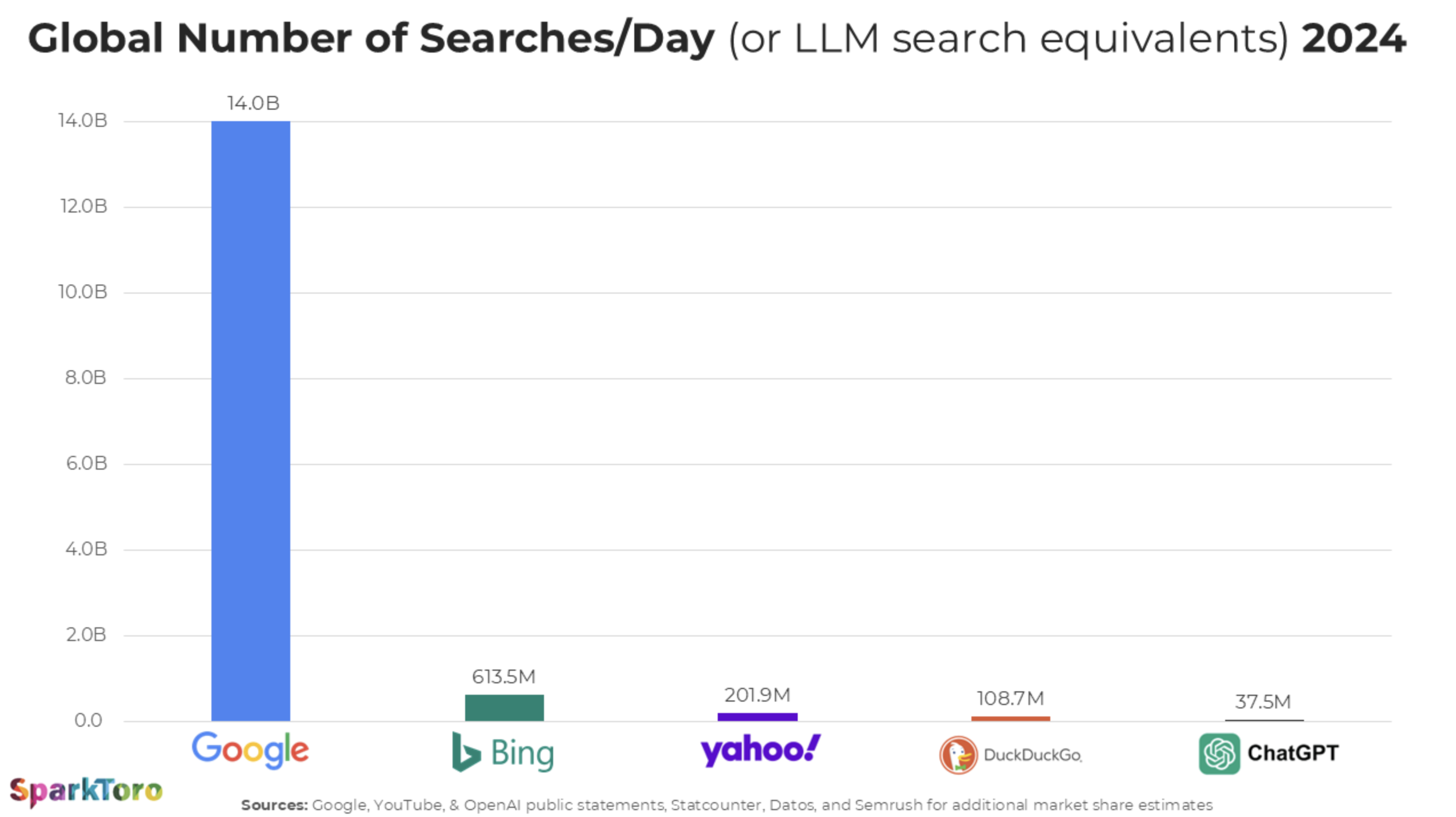
This reinforces the need for brands to invest in SEO services as the vast majority of people will discover new brands and research products and services using Google and other traditional search platforms.
Generative Engine Optimization strategies and tactics
While GEO shares foundational principles with traditional SEO, the specific tactics are starting to diverge — largely because traditional search engines like Google rely on crawling, indexing, and ranking content, while LLMs generate answers by interpreting patterns, semantics, and intent. Because this is a new and evolving space, the generative engine optimization best practices are currently being defined to better align with how AI tools source, understand, and surface content.
Here are several emerging best practices for GEO:
- Follow EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Just like in SEO, content should be written for humans, not just machines — ensuring it’s helpful, readable, and demonstrates deep expertise.
- Highlight the Authority of Authors: Elevate credibility by showcasing the author’s qualifications, credentials, or unique perspectives — this helps both users and LLMs understand trust signals.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: GEO emphasizes natural language and readability; overly optimized content can hurt performance in AI-generated results.
- Use Semantic Associations: Consistently associating your brand with a set of related keywords or themes can train models to recognize your domain authority on a topic.
- Answer Common Questions: Proactively answer frequently asked questions related to your products, services, or industry — this increases your chances of being cited in AI responses.
- Build Focused Content Clusters: Instead of overly long, catch-all posts, break content into tight, topic-specific clusters that clearly signal topical relevance.
- Apply Technical Enhancements: Structured data, schema markup, and even new tools like llms.txt (designed to guide AI crawlers) help ensure your content is readable and accessible to both traditional crawlers and LLMs.
- Deprioritize Link Building (Somewhat): While still useful for SEO, LLMs don’t rely on link graphs as heavily — so internal clarity and topical authority matter more than backlink volume in GEO.
- Align GEO with PR activities: Since LLMs weigh authoritative publications, community discussions such as Reddit, and author profiles highly, public relations efforts are a key input to GEO.
How can I measure the success of my GEO efforts?
Measuring Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) efforts is still a developing practice, and unlike traditional SEO, most AI chat tools like ChatGPT or Perplexity don’t yet offer native analytics to show how often (impressions) or in what context (query/keyword ranking) your brand appears in their generated answers.
However, there are still ways to gauge performance. You can track referral traffic from AI tools with web analytics — we’ve outlined step-by-step instructions for measuring AI traffic here.
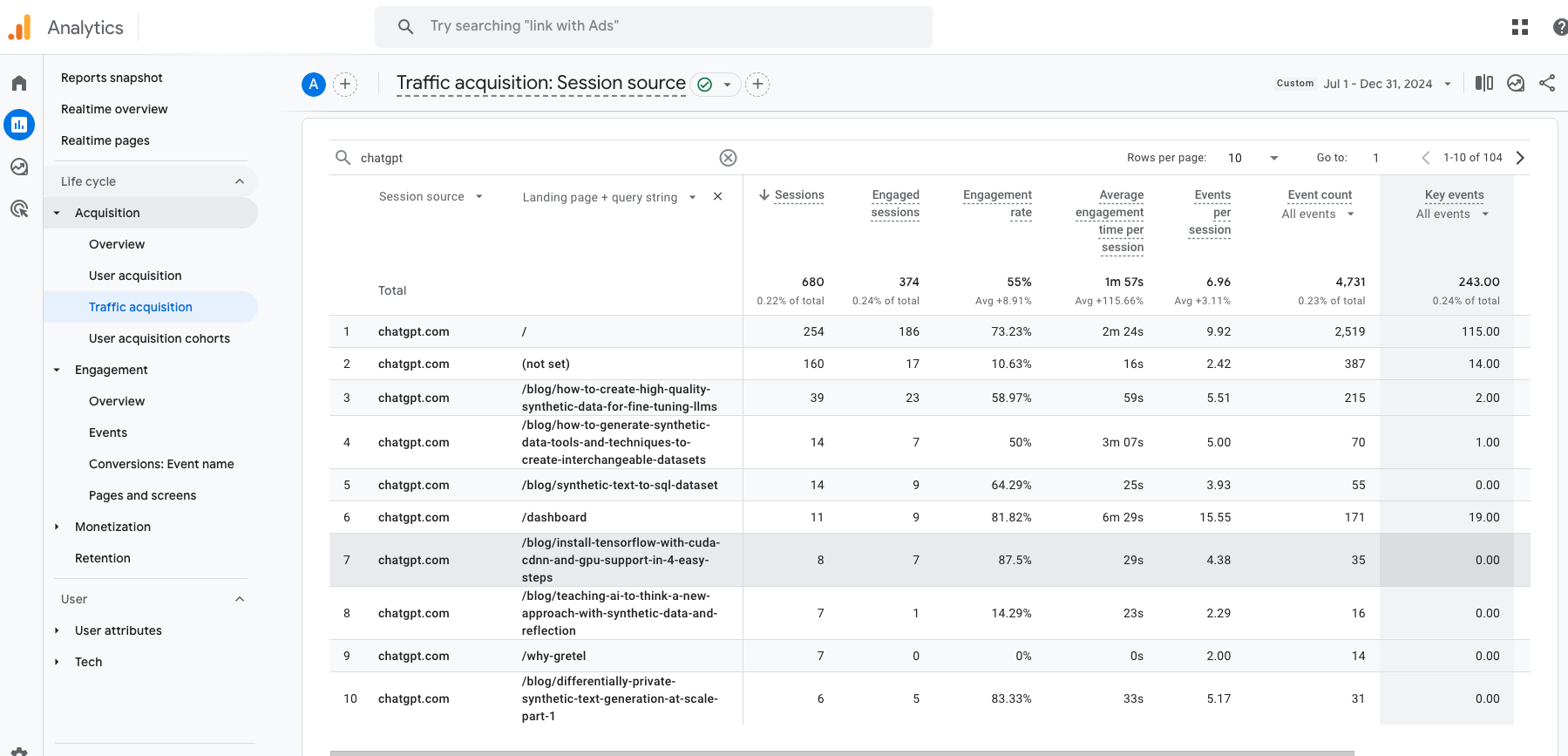
GA4 Reports Traffic Acquisition View
Additionally, SEMrush’s AI Toolkit is beginning to fill some gaps with features like AI Keywords Trending, Market Share in AI Results vs. Competitors, and tools that predict how likely your content is to appear in AI-generated summaries.
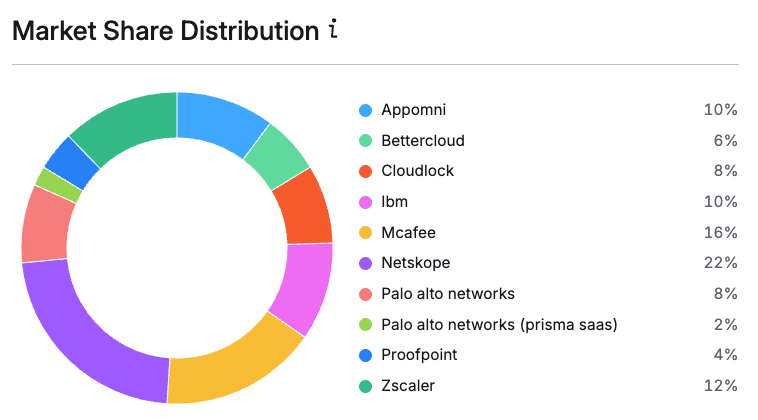
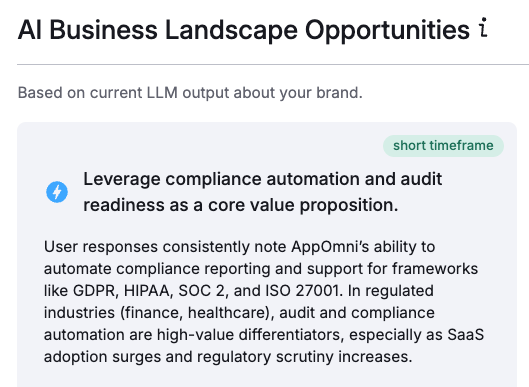
SEMrush AI Insights Market Share & Opportunities
In short, measuring GEO is a moving target, but many SEO metrics — such as organic traffic lifts, content performance, engagement, and branded search trends — still offer valuable signals for how well your content is resonating with both users and machines.
Enlisting the help of Generative Engine Optimization Agencies
As search continues to evolve, so must your strategy. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents the next frontier of organic visibility — where getting cited by AI tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, X.ai’s Grok and Google’s AI Overviews is just as critical as ranking on a traditional SERP.
While many of the foundations of SEO still apply, GEO introduces new rules, new tactics, and new opportunities to stand out in AI-generated responses. From optimizing content structure and semantic relevance to implementing emerging technical standards, staying ahead means being proactive — not reactive.
At Firebrand, we combine deep SEO expertise with cutting-edge generative engine optimization services, purpose-built for B2B tech startups and scaleups. If you’re ready to future-proof your organic strategy and show up where your buyers are searching — human or AI — we’re here to help. Let’s talk.
